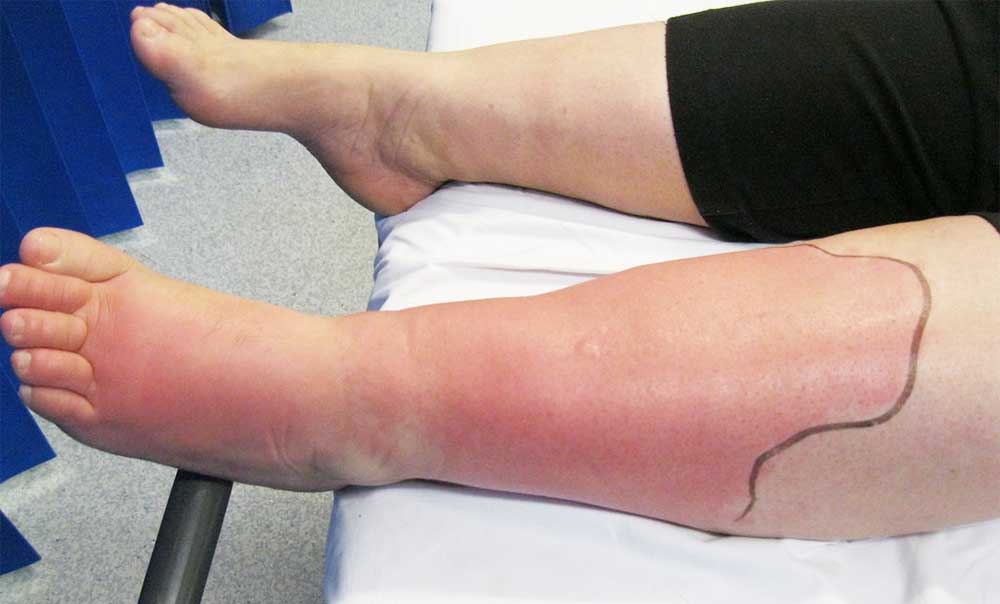
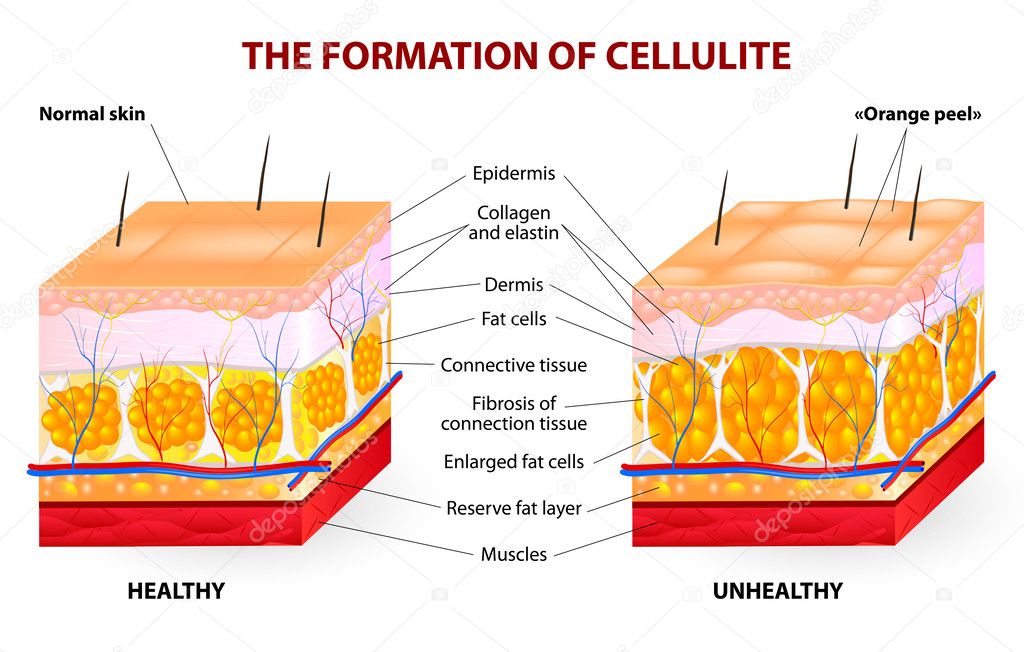
Cellulitis is a common, potentially microbial severe skin infection. The impacted skin shows up swollen and red and is commonly unpleasant and cozy to the touch. Cellulitis naturally influences the skin on the reduced legs. However, it can take place in the face, arms, and also other locations. It takes place when a crack or break in your skin allows bacteria to go inside.
Overlooked, the infection can infect your lymph nodes as well as bloodstream and rapidly become serious. It isn’t generally spread from person to person. Cellulitis may be a common and generally uncomfortable bacterium skin infection. It’s most likely to at first appear like a red, puffy room that feels hot and tender to the little bit. The inflammation and swelling will unravel swiftly. infection is generally on the surface of your skin; however, it will impact the cells conjointly underneath.
It most regularly impacts the reduced legs’ skin, though the infection will occur just about anywhere on your body or face. The infection will unravel to your wit nodes as well as blood.
Causes of Cellulitis
Cellulitis happens when microorganisms, streptococcus, and staphylococcus, enter through any cut or split in your skin. The appearance of more serious staphylococcus infection called methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is increasing.
Although Cellulitis can happen anywhere on your body, the most typical location is the reduced leg. Bacteria are probably to go into disrupted skin locations, such as where you have had recent surgery, cuts, puncture wounds, an ulcer, an athlete’s foot, or dermatitis.
The germs can also go into areas of dehydrated, half-cracked skin or inflamed skin. The occurrence of a lot of severe staph infection known as methicillin-resistant staph aureus (MRSA) is increasing. The bacterium is potentially to enter non contiguous skin locations, like any place you have had recent surgical treatment, cuts, leak injuries, an ulcer, athlete’s foot, or dermatitis. Animal bites can create Cellulitis. Microorganisms can also enter through locations of dry, flaky skin or puffy skin.
Contact Your Doctor if:
You don’t feel higher at intervals three days once beginning antibiotics; your symptoms aggravate you develop a fever. You may have to be enforced to be treated with IV antibiotics during a hospital if you have:
- Warmth in body
- Low pressure
- An infection that doesn’t improve with antibiotics
- Weakened system thanks to alternative diseases
Risk factors
Several factors place you at multiplied risk of Cellulitis:
Skin conditions: Conditions like skin disorder, athlete’s foot, and shingles will cause breaks within the skin that offer bacterium associate entry purposes. Chronic inflammation of your arms or legs (lymphedema). This condition typically follows surgery.
Injury: Any cut, fracture, burn or scrape provides bacterium associate entry purpose
Weaken immune system: Conditions that weaken your systems — like polygenic disease, leukemia, and HIV/AIDS — leave you a lot of at risk of infections. Bound medications can also weaken your system.
Inspect your feet daily:
Frequently check your feet for signs of injury; thus, you’ll catch infections early. Trim your fingernails and toenails rigorously. Moisturize your skin frequently. Lookout to not to injure the encompassing skin. Lubricating your skin helps stop cracking and peeling. Don’t apply moisturizer to open sores. Protect your hands and feet.
Superficial skin infections will unfold from person to person. Wear appropriate footwear and gloves. Diagnosis, Your doctor can probably be ready to diagnose a rubor by staring at your skin. Promptly treat infections on the skin’s surface (superficial), like athlete’s foot. In some cases, they might recommend blood tests or alternative tests to assist rule out other conditions. Don’t wait to start treatment.
Symptoms of Cellulitis
Contact your doctor promptly if you have got any of those symptoms. Cellulitis symptoms include:
- Fever
- Feeling of heat within the affected space
- Skin sore or rash that grows quickly
- Redness or inflammation of your skin
- Tight, glossy, swollen skin
- Tenderness within the affected space
- Any symptom with pus
More serious Cellulitis symptoms include:
- warm skin
- lightheadedness
- dizziness
- fatigue
- muscle aches
- Chills
- Shaking
- feeling unwell
- sweating
Symptoms like these might mean that Cellulitis is spreading:
- Lethargy
- red streaks
- Drowsiness
- Blisters
Prevention
If your Cellulitis recurs, your doctor might suggest preventive antibiotics. To assist stop rubor and alternative infections, take these precautions after you have a skin wound:
- Cover your wound with a bandage.
- Modification bandages a minimum of daily.
- Wash Away your wound daily with soap. Try this gently as a part of your traditional bathing.
- People with polygenic disease and poor circulation must be compelled to take further precautions to forestall skin injury.
- Watch for signs of infection—redness, pain, and emptying all possible signal infection and would like for medical analysis.
- Apply a protecting cream or ointment. For many surface wounds, associate over-the-counter ointment (Vaseline, Polypore, others) provides adequate protection.
Treatment of Cellulitis
Cellulitis treatment involves taking antibiotics orally for five to fourteen days. Rest till your symptoms improve. Your doctor might also dictate pain relievers. Raise the affected limb beyond your heart to scale back swelling. You would possibly like more prolonged treatment if your infection is severe, thanks to a chronic condition or a weakened system.
Cellulitis ought to escape at intervals seven to ten days once you begin taking antibiotics. This can ensure all the bacteria are gone. Even if your symptoms improve at intervals many days, take all the antibiotics your doctor prescribed.
Its therapy involves taking prescription antibiotics by mouth for 5 to 14 days. Your doctor may likewise prescribe pain relievers. Relax till your signs and symptoms enhance. Elevate the damaged limb more than your heart to lower swelling.
Cellulitis ought to go away within 7 to 10 days after you start taking prescription antibiotics. You might require more prolonged therapy if your infection is severe because of a persistent condition or a weakened body immune system. Even if your signs and symptoms enhance within a few days, take all your doctor’s antibiotics. This will ensure every one of the microorganisms is gone.
Get in touch with your doctor if:
- You don’t feel better within three days after beginning antibiotics
- Your symptoms get worse
- High temperature
If the infection isn’t regrettable, you can take antibiotics by mouth for a week to 2 weeks. Your medical professional will certainly arrange a follow-up appointment. They may make use of IV or intramuscular antibiotics if:
- The infection is severe.
- You have other clinical problems.
- You’re very young or older.
- The Cellulitis covers significant areas, gets on your hands, or is close to body components like your eyes.
- The infection intensifies even after taking antibiotics for 2 to 3 days.
In severe instances, you may need to stay in the medical facility. You’ll obtain IV prescription antibiotics until the infection is controlled (2 to 3 days), and then go house with oral medications.
Takeaway
Cellulitis may be a common microorganism infection that will develop from a cut, scrape, or wound, like a bug bite. Microorganism will enter that gap and transform an infection. Once associate degree insect bites or stings you, a small hole forms in your skin.
Likewise, scratching or itch a bug bite will tear the skin that conjointly creates a gap for microorganisms. Create an arrangement to envision your doctor if you develop these symptoms. When associate degree infection develops in your deepest skin layers, you’ll expertise redness, swelling, and inflammation around the bite.